Every day you check Gmail, watch YouTube, shop on Amazon… and without even realizing it, you’re already using dozens of web applications! But do you know how web apps work and what the best examples of future articles are in 2025? We’ll explain everything.
Today, web applications are very important in our digital world. Unlike old-style software that you need to install on your computer, web applications run in your internet browser. This means you can use them from almost anywhere. For example, people use them to manage daily tasks or watch movies online. As a result, web apps have become a big part of everyday life. Whether you’re looking for the newest web application tools or trying to understand the difference between a website and a web app, more and more people depend on them. Some popular examples include Google Workspace, Netflix, and the Kindle web app — all showing how useful and flexible web applications can be.
What Are Web Applications?
Web applications (or web apps) are software programs that run in a web browser instead of being downloaded and installed on a device. You can open them using the internet, just like you open a website. However, web apps are interactive — they let you do things, not just read or watch.
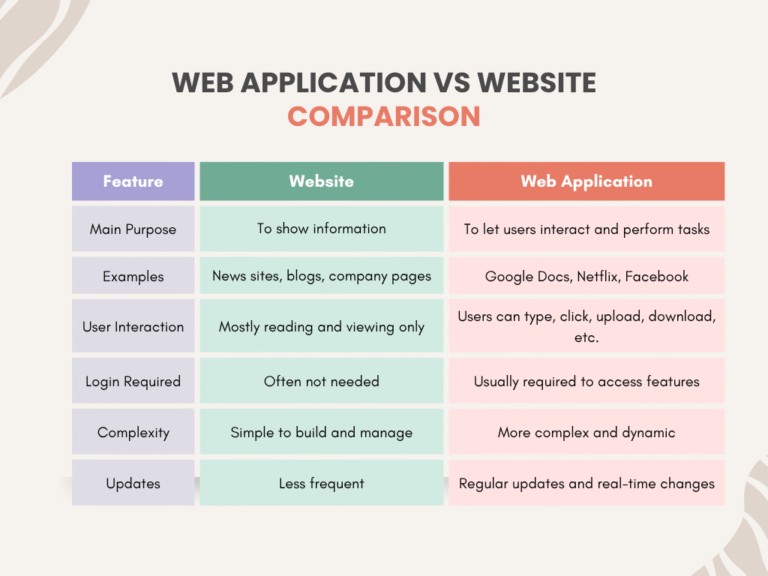
Web Application vs Website
A common question is the debate of web application vs website. While a website primarily presents information, a web application allows dynamic interactions, such as submitting forms, processing data, or collaborating in real time.
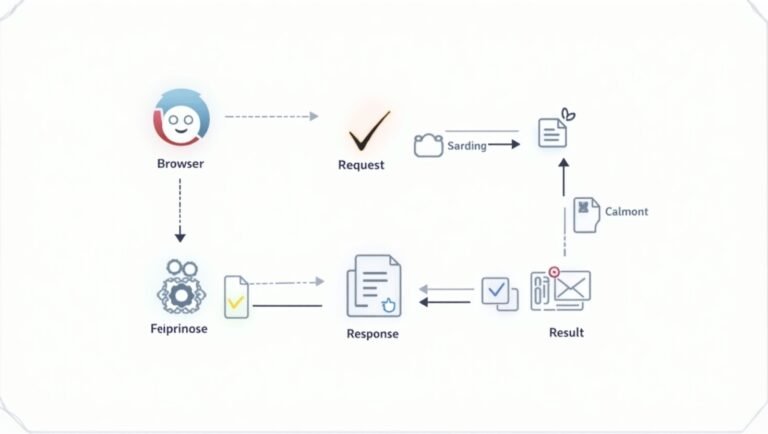
How Do Web Applications Work?
Ever wondered how web applications work? Let’s break it down. First, you open the web app in your browser (like Chrome or Safari). Then, when you click or type something, the app sends a request to a server over the internet. Next, the server processes your request — like saving a file or loading new data. After that, the server sends a response back to the browser, which shows the result on your screen. All of this happens very fast, and usually, you don’t even notice it — it works smoothly in the background.
.
Why Modern Web Applications Are So Useful:
Modern web applications are popular for many reasons.
First of all, they are easy to access. You can open apps like Outlook Web or Facebook on any device that has internet, using just a browser.
Secondly, they work well on all kinds of devices — laptops, smartphones, and tablets. This means you get the same experience no matter what you use.
Another big benefit is that you don’t need to install anything. Unlike desktop software, web apps run directly in the browser. There’s no need to download large files.
Finally, web apps are easy to update. Developers can quickly add new features or fix security issues for all users at once.
Benefits of Web Applications for Businesses and Users:
Web applications are helpful for both companies and everyday users.
To begin with, they are cost-effective. Businesses don’t have to spend a lot of money on installing, updating, or maintaining software.
Next, they offer remote access. This means teams can work together from anywhere in the world using tools like Slack or Trello.
In addition, web apps are easy to maintain. Since updates happen on the company’s server, users don’t have to worry about doing anything themselves.
Lastly, web apps improve teamwork. For example, Google Workspace lets several people edit the same document at the same time — making collaboration fast and easy.
Popular Examples of Web Applications
Many people use web applications every day, often without even realizing it. Here are some well-known examples:
First, Google Workspace (like Docs and Sheets) lets you create and edit documents or spreadsheets online.
Next, Facebook is a social media platform that helps billions of people stay connected.
Then, tools like Slack make it easier for teams to communicate and work together.
Also, Trello is a simple, visual tool for managing projects and tasks.
In addition, online shopping platforms like Shopify and Magento help businesses run their stores over the internet.
Another great example is Netflix, which streams movies and shows using dynamic content.
Lastly, the Kindle web app allows you to read eBooks right in your browser — no Kindle device needed.
So, if you’re still wondering, “Is Google a web application?” or “Is Netflix a web application?” — the answer is yes! They are some of the best examples of modern, powerful web apps.

Types of Web Applications:
Web apps come in many forms, including:
Static web apps: Simple pages that display the same content to every visitor.
Dynamic web apps: Content updates based on user interactions or database queries.
Single Page Applications (SPAs): Apps like Gmail that dynamically rewrite the current page without loading new pages from the server.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Apps that behave like native mobile apps but run in browsers, even offline.
E-commerce apps: Platforms like Magento or Shopify that enable online shopping.
Portal web apps: Central hubs offering multiple services, like news, email, or user dashboards.
How Web Applications Are Developed
Building a web application takes different tools and steps.
First, developers create the front end — the part users see and click on. They use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks to design this part.
Next, the back end handles how the app works behind the scenes. Developers use languages like Node.js, Python, PHP, or Ruby to manage this.
Then, they use databases to store and organize the app’s data. This is important for apps that show changing or personalized content.
Also, developers think about security. Tools like a web application firewall or AWS WAF help keep the app safe from hackers.
Some people may wonder, “Is Java only for hardware or big systems?” Java is also very popular for web apps, especially when building powerful back-end services.

Trends Shaping Web Applications in 2025 and Beyond:
Web technology keeps changing, and some important trends are shaping the future.
The rise of PWAs for faster, app-like experiences.
First of all, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are becoming more popular. They work faster and feel like real mobile apps.
Next, more web apps are using AI and machine learning. This helps apps become smarter by giving users personalized content and useful data insights.
Also, there is a stronger focus on security. Tools like web application firewalls are being used to protect apps from online attacks.
In addition, low-code and no-code platforms are growing fast. These tools let people who aren’t developers create their apps easily.
Finally, developers are paying more attention to user experience (UX/UI). This means making apps that are simple to use and look good, too.
FAQs about Web Applications:
Q: What is a web application?
A web application is software that runs on a server and is accessed via a browser. Examples include Gmail, Netflix, and Google Docs.
Q: What are examples of web applications?
Popular web applications include Gmail, Facebook, Netflix, Amazon, and Google Docs. These tools allow users to work and interact online.
Q: What are the benefits of web applications?
Web apps are cost-effective, easy to update, mobile-friendly, and accessible from any device with an internet connection.
Q: What are the top web application trends in 2025?
Top trends include AI-driven apps, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), cloud-based solutions, enhanced security, and mobile-first design.”
Q: Is Netflix a web application?
Absolutely. Netflix is a dynamic web app delivering video streaming directly in your browser.
Glossary of Web Application Terms:
Web Application Firewall (WAF): A security tool that filters and monitors HTTP traffic.
PWA: Progressive Web Application, blending web and native app experiences.
SPA: Single Page Application, where navigation happens without full page reloads.
Conclusion
Today, web applications have changed the way people communicate, work, and have fun. For example, simple apps can show basic information, while advanced platforms like Netflix or the Outlook Web App offer powerful features. This shows how many things are possible with web apps.
For businesses and developers, it’s very important to understand how web apps are made and to follow the latest trends. This way, they can stay successful and keep up in the fast-changing digital world.







Add comment